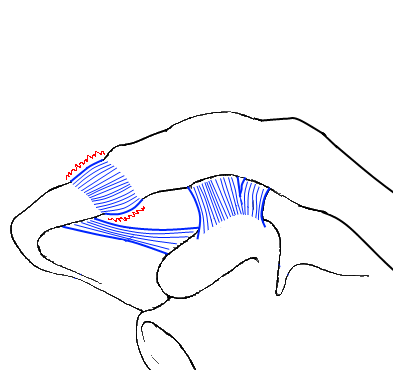
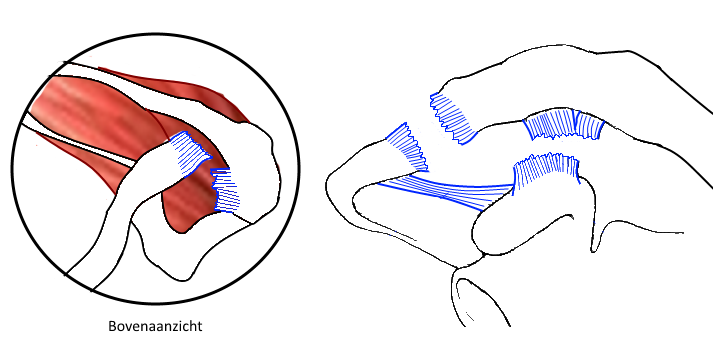
Acromioclaviculaire luxatie
Acromioclaviculaire luxatie
Auteur: J. Sprakel, MD - Laatste update: 21-10-2014
Acromioclaviculaire luxatie
Diagnostiek
- Standaard röntgenopnames
- - X-schouder AP met hangende armen
- - Bij twijfel vergelijkbare opname van de niet aangedane zijde maken
- - Zanca opname: 10‐15 graden schuin ingeschoten, caudo-craniaal
- - Axillaire opname: posterior verplaatsing bij type IV
- - Stress opnames hebben geen klinische relevantie en worden niet gemaakt
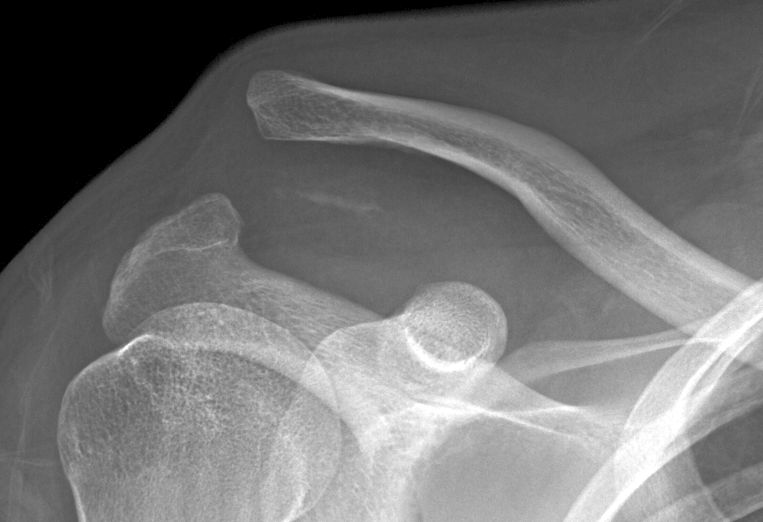
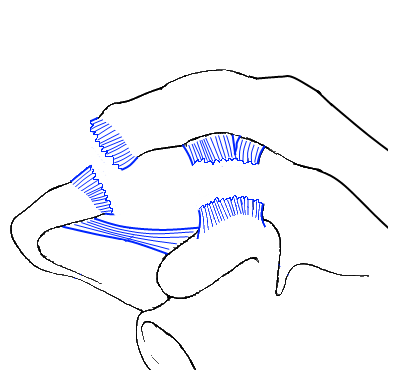
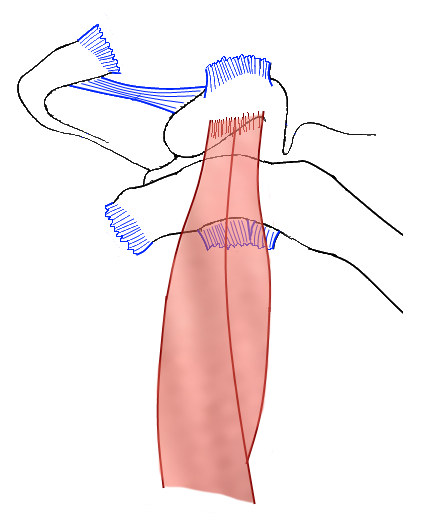
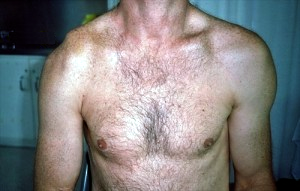
AC-luxatie Tossy 3: Hover over de afbeelding om bevindingen te zien
Classificatie
Classificatie volgens Tossy 1 en/of Rockwood 2Conservatieve behandeling
- Indicaties:
- - Tossy 1
- - Tossy 2
- - Tossy 3
- - Tossy 4
- (Na-)behandeling:
- - 1-2 week sling/mitella
- - Na 1‐2 weken functioneel op geleide van pijn
- - Patiënt inlichten over persisteren van "bult" bij Tossy 2 en 3
- - Langdurig bestaan (meestal 3‐6 maanden) van klachten bij Tossy 3
- Follow-up:
-
Poliklinische follow‐up Na 10 dagen Na 4 weken Na 6 weken Na 3 maanden (op indicatie) - Functiecontrole
- Oefeninstructies- Functiecontrole
- Fysiotherapie op indicatie
- Evt. ontslag controle indien geen klachten en goede functie- Functiecontrole
- Fysiotherapie op indicatie
- Evt. ontslag controle indien geen klachten en goede functie- Functiecontrole
- Bij persisterende klachten overweeg herstel AC ligamenten
Functiecontrole:
Duur tot herstel:
- - Bij conservatieve behandeling 6‐12 weken geen zwaar werk/contactsport.
- - De herstelduur bij een Tossy 3 letsel is hoger enbedraagt 3‐6 maanden.
Operatieve behandeling
- Relatieve indicaties:
- - Tossy 3
- - Tossy 4
- Absolute indicaties:
- - Tossy 5-6
(Na-)behandeling:
- - Verkrijgen oefenstabiele fixatie, evt. met primair herstel of reconstructie AC en CC ligament
- - Open repositie en stabilisatie met haakplaat of Coraclaviculaire sling
- - Vermijd transarticulaire osteosynthese
-
- - Bij chronische luxatie: Weaver-Dunn procedure of Coracoclaviculaire stabilisatie (Sling met tightrope) gecombineerd met autologe semitendinosuspees
-
- - Afhankelijk van de gebruikte techniek, doorgaans oefenstabiele osteosynthese
- - 6 weken onbelast
- - X‐controle op dag 1 postoperatief
- - Oefeninstructies door zaalarts of fysiotherapeut
Follow-up:
-
Poliklinische follow‐up Na 10 dagen Na 4 weken Na 6 weken Na 3 maanden (op indicatie) - Hechtingen verwijderen
- Oefeninstructies- X-controle
- Functiecontrole
- Fysiotherapie op indicatie- Op indicatie bij klachten
- X-controle
- Functiecontrole
- Oefeninstructies
- Fysiotherapie op indicatie
- Evt. plannen voor VOSM
Functiecontrole:
Complicaties
- Conservatieve behandeling:
- - Arthrose (A‐C gewricht)
- - Pijn
- - Functio laesa
- Operatieve behandeling:
- - Functio laesa
- - Peristerende klachten
- - Infectie)
- - (Na-)bloeding
- - Wondinfectie
- - Uitbreken osteosynthese materiaal/falen fixatie
- - Zenuwletsel (rami van de nn. supraclacivulares)
- - Pijnklachten en/of functieverlies ondanks geslaagde ingreep
- - Arthrose
- Specifiek voor haakplaat (schouder klachten):
- - Subacromiale impingement
- - Tendinitis
- - Frozen shoulder (verdwijnt na VOSM)
Patiëntenvoorlichting

| Voorlichtingsfolder Oefeningen Schouder (Word) |

| Voorlichtingsfolder Oefeningen Schouder (PDF) |
Coderingen
Diagnose Behandel Combinatie (DBC/DOT)
ICD-10
| Chirurgie | 255 |
| Orthopedie | 3201 |
ICD-10
| Subluxatie en luxatie van acromioclaviculaire gewricht | S43.1 |
Abbreviated Injury Scale (AIS)
| Acromioclavicular joint - sprain | 770710.1 |
| Acromioclavicular joint - subluxation | 770720.1 |
| Acromioclavicular joint - dislocation | 770730.2 |
| Acromioclavicular joint - dislocation - open | 770731.2 |
| Acromioclavicular joint - open | 770789.1 |
| Acromioclavicular joint NFS | 770799.1 |
Referenties
- 1. Tossy JD, Mead NC, Sigmond HM. Acromioclavicular separations: useful and practical classification for treatment. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1963;28:111-9.
- 2. C.A. Rockwood Jr., D.P. Green Injuries to the acromioclavicular joint: Subluxations and dislocations about the shoulder Fractures in adults JB Lippincott, Philadelphia (1984), pp. 860–910