GIST
GIST
Auteur: J. Sprakel, MD - Laatste update: 14-05-2020
GIST
Algemeen
- - Meest voorkomende mesenchymale tumor van tractus digestivus
- - Definitie GIST: KIT (CD117, stem cell factor receptor)- positieve mesenchymale spindle cell or epithelioid neoplasmata 4
- - Incidentie: 15 per miljoen per jaar 1
- - GIST tumorgenese vanuit Interstitiele Cellen van Cajal (ICC) en hangt af van de transcriptie van factor ETV1 13
- - ICC: elektrische pacemaker van tractus digestivus (peristaltiek), interface tussen de autonome innervatie van de darmwand en het gladde spierweefsel
- - KIT protein (CD117) zit op ICCs
- - 20-30% zijn maligne tumoren
- - Leeftijd: >50 jaar - voornamelijk tussen 55-65 jaar 6
- Distributie anatomische lokatie 3 :
- - Maag (50-60%)
- - Dunne darm (20-30%)
- - Colon en rectum(10%)
- - Oesofagus (5%)
- - Elders intra-abdominaal, mesenterium, omentum en retroperitoneum (5%)
Klinische presentatie
- Asymptomatisch als toevalsbevinding:
- - bij endoscopische onderzoek in wand van slokdarm of duodenum 2
- - bij laparotomie/laparoscopie in de wand van dunne darm of maag
- - bij rectaal toucher bij prostaat- of gynaecologische onderzoek van rectale GIST tumoren
- - bij X-thorax als oesofageale massa
- Symptomatisch:
- - Dysfagie bij GIST in oesofagus
- - Hoge GI bloeding bij GIST in maag en dunne darm
- - Lage GI bloeding, darmperforatie, pijn, obstructie of combinatie hiervan bij GIST in colon
- - Zelden extern palpabel (dan vaak malignne)
Diagnostiek
- - Lab: algemeen bloedbeeld / chemie
- - CT-thorax abdomen met iv-contrast
- - Verkrijgen / revisie van PA (bij voorkeur histologie) + mutatie-analyse
- - Voorkeur middels endo-echografie met transluminale biopsie
- - Indien endo-echo niet mogelijk dan primaire resectie middels laparoscopie of laparotomie
- - Percutane biopsie bij gemetastaseerde of inoperabele tumoren (voorkeur altijd endo-echo)
- Op indicatie:
- - MRI rectum bij rectale GIST
- - FDG-PET-CT scan bij metastasen of indien R0 resectie niet mogelijk is (locally advanced)
Behandeling
- Gespecialiseerd GIST-centrum:
- - Multidisciplinaire beoordeling in GIST-centrum voor behandeladvies/behandeling (AvL Amsterdam, UMCG, LUMC, Radboud, Erasmus)
- Conservatief
- - Tumoren <2cm: vervolgen via endoechografie en bij groei verwijderen
- - Indien er majeure chirurgie moet worden verricht (Whipple/PPPD e.d.)
- Gelocaliseerde ziekte
- - Tumoren >2cm
- - Primaire behandeling van niet gemetastaseerde GIST: complete chirurgische verwijdering 9
- - Orgaansparende excisie, marge van enkele millimeters is voldoende
- - Oesofagusresectie bij GIST in oesofagus
- - Zelden Whipple/PPPD bij GIST in duodenum
- - Bij R1 resectie overwegen re-excisie, mits de resttumor verdacht gebied terug gevonden kan worden en verwijderd zonder majeure functionele gevolgen
- - Voorkeur: "open" resectie, bij makkelijk gelegen GIST tumoren dan overwegen laparoscopisch excisie 9
- - Adjuvante therapie met Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor (TKI) bij High Risk Tumoren volgens Miettinen
- Locally advanced ziekte
- - Neoadjuvante behandeling met een Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor (TKI) kan bij locally advanced ziekte de resectabiliteit verbeteren
- - Rectum en cardia GIST vaak neo-adjuvante behandeling
- - Indien niet mogelijk om orgaansparend te opereren of indien multiviscerale resectie nodig is
- - Maximale bereikbare respons na 6-12 maanden, gevolgd door resectie
- - Monitoring repons met CT met iv-contrast of FDG-PET-CT scan (vnl bij locally advanced) 10
- - Respons-monitoring met Choi-criteria: afname in GIST grootte >10% of afname in tumor densiteiti op CT >15% 12
- Gemetastaseerde ziekte
- - Palliative behandeling met Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor (TKI) via medische oncologie
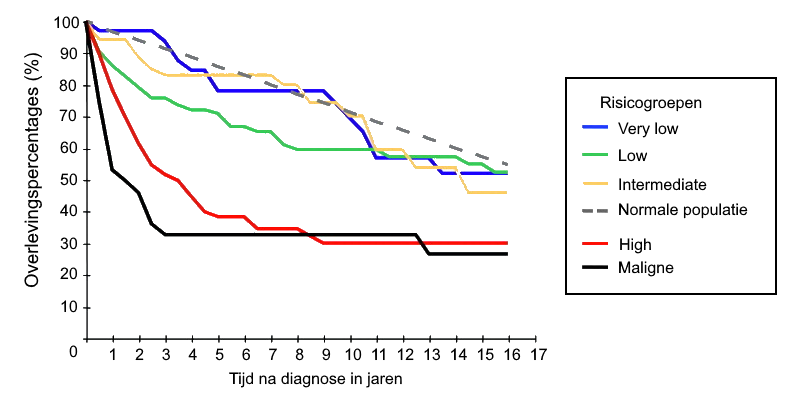
Adjuvante therapie - Risicoclassificatie Miettinen
- Indicatie:
- - High risk tumoren volgens Risicoclassificatie Miettinen - >50% kans op recidief
- - Per-operatieve tumorperforatie
| Risicoclassificatie volgens Miettinen voor selectie van adjuvante therapie bij GIST tumoren 8 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tumor parameters | Risico op lokaal recidief / metastasen (%) | |||||||||
| Groep | Tumor grootte (cm) |
Mitotische index (per 50 HPF) |
Maag | Dunne darm | Duodenum | Rectum | ||||
| 1 | ≤2 cm | ≤5 | None (0%) | |||||||
| 2 | >2 - ≤5 cm | ≤5 | Very low | (1,9%) | Low | (4,3%) | Low | (8,3%) | Low | (8,5%) |
| 3a | >5 - ≤10cm | ≤5 | Low | (3,6%) | Moderate | (24%) | High | (34%) | High | (57%) |
| 3b | >10 cm | ≤5 | Moderate | (12%) | High | (52%) | High | (34%) | High | (57%) |
| 4 | ≤2 cm | >5 | None * | (0%) | * | (50%) | ** | ** | High | (54%) |
| 5 | >2 - ≤5 cm | >5 | Moderate | (16%) | High | (73%) | High | (50%) | High | (52%) |
| 6a | >5 - ≤10 cm | >5 | High | (55%) | High | (85%) | High * | (86%) | High * | (71%) |
| 6b | >10 cm | >5 | High | (86%) | High | (90%) | High * | (86%) | High * | (71%) |
** Geen tumoren in serie met deze parameters
- 1ste lijn - Imatinib (Glivec®):
- - Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor, STI-571
- - Blokkeert ATP binding aan tyrosine kinase, inhibeert het geactiveerde KIT protein (CD117)
- - Induceert apoptose in KIT+ GIST cellen
- - Bijwerkingen: misselijkheid, vochtretentie (periorbitaal oedeem, congestief hartfalen), verlengde QT tijd - dosisaanpassing of tijdelijk staken
- - PDGFRA-mutatie: D842V of D842I puntmutaties - reageert niet op Imatinib
- Dosering Imatinib:
- - Imatinib 1dd400mg voor 3 jaar (inclusief neo-adjuvante periode meegerekend)
- - Dosering op geleide van bloedspiegel Imatinib
- - Streefwaarde dalspiegel Imatinib: >1000 ng/ml 11
- - Uitzondering: Exon 9 mutaties - dosis evt. ophogen naar 1dd800mg
- 2de lijn - Sunitinib (Sutent®)
- - Falen van Imatinib, als gevolg van resistentie of intolerantie
- - Sunitinib 1dd 37,5mg of alternatief schema: 1dd 50mg (4 weken behandeling / 2 weken zonder) óf (2 weken behandeling / 1 week zonder)
- - Dosering op geleide van bloedspiegel Sunitinib
- - Therapeutisch spiegel: 37,5 - 75 ng/ml bij alternatief schema: 50 - 75 ng/ml
- 3de lijn - Regorafenib (Stivarga®)
- - Bij gevorderd stadium na falen van Imatinib en Sunitinib
- - 1 behandelcyclus (4 weken): 1dd160mg gedurende 3 weken, gevolgd door 1 week zonder behandeling
Follow-up
High Risk GIST tumoren:| Tijd post-OK | Lichamelijk onderzoek | Lab (Bloedbeeld, Chemie, Imatinib-spiegel) | CT-abdomen | Lastmeter | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | weken | Normale post-op controle | |||||
| 3 | maanden | X | X | ||||
| 6 | maanden | X | X | ||||
| 9 | maanden | X | X | ||||
| 1 | jaar | X | X | X | X | ||
| 1 | jaar | 3 | maanden | X | X | ||
| 1 | jaar | 6 | maanden | X | X | ||
| 1 | jaar | 9 | maanden | X | X | ||
| 2 | jaar | X | X | X | X | ||
| 2 | jaar | 3 | maanden | X | X | ||
| 2 | jaar | 6 | maanden | X | X | ||
| 2 | jaar | 9 | maanden | X | X | ||
| 3 | jaar | X | X | X | X | ||
| 3 | jaar | 6 | maanden | X | X | ||
| 4 | jaar | X | X | X | |||
| 4 | jaar | 6 | maanden | X | X | ||
| 5 | jaar | X | X | X | |||
| 5 | jaar | 6 | maanden | X | X | ||
| 6 | jaar | X | X | X | |||
| 7 | jaar | X | X | X | |||
| 8 | jaar | X | X | X | |||
| 9 | jaar | X | X | X | |||
| 10 | jaar | X | X | X | |||
Intermediate Risk GIST tumoren:
| Tijd post-OK | Lichamelijk onderzoek | CT-abdomen | Lastmeter | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | weken | Normale post-op controle | ||||
| 4 | maanden | X | X | |||
| 8 | maanden | X | X | |||
| 1 | jaar | X | X | X | ||
| 1 | jaar | 4 | maanden | X | X | |
| 1 | jaar | 8 | maanden | X | X | |
| 2 | jaar | X | X | X | ||
| 2 | jaar | 4 | maanden | X | X | |
| 2 | jaar | 8 | maanden | X | X | |
| 3 | jaar | X | X | X | ||
| 4 | jaar | X | X | X | ||
| 5 | jaar | X | X | X | ||
| 6 | jaar | X | X | X | ||
| 7 | jaar | X | X | X | ||
| 8 | jaar | X | X | X | ||
| 9 | jaar | X | X | X | ||
| 10 | jaar | X | X | X | ||
Low Risk GIST tumoren:
| Tijd post-OK | Lichamelijk onderzoek | CT-abdomen | Lastmeter | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | weken | Normale post-op controle | ||||
| 1 | jaar | X | X | X | ||
| 2 | jaar | X | X | X | ||
| 3 | jaar | X | X | X | ||
| 4 | jaar | X | X | X | ||
| 5 | jaar | X | X | X | ||
Very low Risk GIST tumoren:
- Geen follow-up
Patientenvoorlichting
- - Patientenplatform Sarcomen - Leven met GIST
- - Website: https://www.contactgroepgist.nl/
Complicaties
- Korte termijn:
- - Afhankelijk van lokatie GIST ("tailor-made")
- - Tumorruptuur (<5%) bij operatie 7
- - R1-resectie (6,1%) 14
- Lange termijn:
- - Afhankelijk van lokatie GIST ("tailor-made")
- - Recidief lokatie: Peritoneum (64%), levermetastasen (50%) of beide (19%) 14
- - Zeldzame lokaties: Lymfklieren (2,3%) bot- (1,1%) en longmetastasen (0,7%) 14
Referenties
- 1. Nilsson B, Bumming P, Meis-Kindblom JM, Oden A, Dortok A, Gustavsson B, Sablinska K, Kindblom LG.Gastrointestinal stromal tumors: the incidence, prevalence, clinical course, and prognostication in the preimatinib mesylate era--a population-based study in western Sweden. Cancer. 2005 Feb 15;103(4):821-9.
- 2. DeMatteo RP, Lewis JJ, Leung D, Mudan SS, Woodruff JM, Brennan MF.Two hundred gastrointestinal stromal tumors: recurrence patterns and prognostic factors for survival. Ann Surg. 2000 Jan;231(1):51-8.
- 3. Fletcher CD, Berman JJ, Corless C, Gorstein F, Lasota J, Longley BJ, Miettinen M, O Leary TJ, Remotti H, Rubin BP, Shmookler B, Sobin LH, Weiss SW.Diagnosis of gastrointestinal stromal tumors: A consensus approach. Hum Pathol. 2002 May;33(5):459-65.
- 4. Miettinen M, Lasota J. Gastrointestinal stromal tumors--definition, clinical, histological, immunohistochemical, and molecular genetic features and differential diagnosis. Virchows Arch. 2001 Jan;438(1):1-12.
- 5. Joensuu H. Risk stratification of patients diagnosed with gastrointestinal stromal tumor. Hum Pathol. 2008 Oct;39(10):1411-9.
- 6. Miettinen M, Sarlomo-Rikala M, Lasota J. Gastrointestinal stromal tumors: recent advances in understanding of their biology. Hum Pathol. 1999 Oct;30(10):1213-20.
- 7. Takahashi T, Nakajima K, Nishitani A, Souma Y, Hirota S, Sawa Y, Nishida T. An enhanced risk-group stratification system for more practical prognostication of clinically malignant gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Int J Clin Oncol. 2007 Oct;12(5):369-74. Epub 2007 Oct 22.
- 8. M Miettinen, J Lasota Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 2013 Jun; 42(2): 399–415.
- 9. Hohenberger P, Ronellenfitsch U, Oladeji O, Pink D, Ströbel P, Wardelmann E, Reichardt P. Pattern of recurrence in patients with ruptured primary gastrointestinal stromal tumour. Br J Surg. 2010 Dec;97(12):1854-9.
- 10. Holdsworth CH, Badawi RD, Manola JB, Kijewski MF, Israel DA, Demetri GD, Van den Abbeele AD. CT and PET: early prognostic indicators of response to imatinib mesylate in patients with gastrointestinal stromal tumor. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2007 Dec;189(6):W324-30.
- 11. Demetri GD, Wang Y, Wehrle E, Racine A, Nikolova Z, Blanke CD, Joensuu H, von Mehren M. Imatinib plasma levels are correlated with clinical benefit in patients with unresectable/metastatic gastrointestinal stromal tumors. J Clin Oncol. 2009 Jul 1;27(19):3141-7.
- 12. Choi H, Charnsangavej C, de Castro Faria S, Tamm EP, Benjamin RS, Johnson MM, Macapinlac HA, Podoloff DA.CT evaluation of the response of gastrointestinal stromal tumors after imatinib mesylate treatment: a quantitative analysis correlated with FDG PET findings. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2004 Dec;183(6):1619-28.
- 13. Chi P, Chen Y, Zhang L, Guo X, Wongvipat J, Shamu T, Fletcher JA, Dewell S, Maki RG, Zheng D, Antonescu CR, Allis CD, Sawyers CL. ETV1 is a lineage survival factor that cooperates with KIT in gastrointestinal stromal tumours. Nature. 2010 Oct 14;467(7317):849-53.
- 14. Cavnar MJ, Seier K, Curtin C, Balachandran VP, Coit DG, Yoon SS, Crago AM, Strong VE, Tap WD,4, Gonen M, Antonescu CR, Brennan MF, Singer S, DeMatteo RP. Outcome of 1000 Patients With Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor (GIST) Treated by Surgery in the Pre and Post-imatinib Eras. Ann Surg. 2019 Apr 2.